
Indian Space Programme and its ecosystem have been in a state of unprecedented vibrancy with various achievements. A glimpse of key milestones embraced by the department since 2014 till date is highlighted as below:
Key missions
Altogether 44 spacecraft missions, 42 launch vehicle missions and 5 technology demonstrators have been successfully realized, since 2014 till date.
In January 2014, the first successful flight with an indigenous Cryogenic Upper Stage, in the GSLV-D5 launch vehicle was achieved and GSAT-14 was placed into GTO.
In September 2014, India’s Mars Orbiter Spacecraft successfully entered into an orbit around planet Mars, putting India into a league of select nations which had sent a spacecraft to the Red Planet. The spacecraft is still functional even after 7 years of operation against the designed life of 6 months and serves the nation with a lot of interesting scientific data.
In December 2014, the country witnessed the experimental flight of the next-generation launch vehicle – the GSLV MKIII. The LVM3-X/CARE Mission, the first experimental suborbital flight of the vehicle, launched the Crew Module Atmospheric Re-entry Experiment (CARE).
AstroSat launched by PSLV in September 2015, is the first dedicated Indian astronomy mission aimed at studying celestial sources in X-ray, optical and UV spectral bands simultaneously. AstroSat has made major breakthroughs by discovering five new galaxies.
ISRO has established and operationalised Navigation with Indian Constellation (NavIC) which provides highly accurate Position, Navigation and Time information to users in India and its surroundings. A total of 7 satellites form the Indian Regional Navigation Satellite System [IRNSS] – all launched by PSLV, with IRNSS-1G completing the constellation in 2016.
Various NavIC based services have been rolled out in many key sectors like - integration of NavIC-enabled devices with the enrolment architecture of UIDAI Aadhar enrolment, incorporation of NavIC in the Continuously Operating Reference Stations (CORS) network, In agricultural drones and Radio Technical Commission for Maritime Services (RTCM) etc.
Successful flight testing of Reusable Launch Vehicle-Technology Demonstrator (RLV-TD) was done on May 23, 2016 from Satish Dhawan Space Centre (SDSC) SHAR, Sriharikota. RLV-TD is one of the most technologically challenging endeavours of ISRO towards developing essential technologies for a fully reusable launch vehicle to enable low-cost access to space.
The first experimental mission of ISRO’s Scramjet Engine towards the realisation of Air Breathing Propulsion System was also successfully conducted in 2016 from SDSC SHAR, Sriharikota.
In 2017, PSLV C-37 created a world record by successfully placing 104 satellites in orbit during a single launch. As an idea mooted by the Hon’ble Prime Minister in the 18thSAARC summit, ISRO has launched the 2.2 Ton communication satellite in 2017 to support neighbouring countries.
The first developmental mission of GSLV Mk-III D1 was successfully accomplished in June 2017 and boosted the GSAT-19 satellite into a geosynchronous transfer orbit.
ISRO demonstrated a crucial technological element of Human spaceflight in July 2018- The Pad Abort Test (PAT) to qualify the Crew Escape System (CES). The Pad Abort Test flight was a demonstration of the capability of CES to evacuate the Crew in case of a contingency at the launch Pad.
In the Independence Day address – 2018, the Hon’ble Prime Minister announced the "Gaganyaan Programme", marking India’s foray into the new age of human space exploration.
GSAT-29 high throughput communication satellite was successfully launched on November 14, 2018, on-board GSLV Mk III-D2. It is providing satellite-based connectivity to Jammu & Kashmir and North Eastern regions of India.
In 2018, ISRO’s next-generation high throughput communication satellite, GSAT-11 was successfully launched on December 05, 2018 from Kourou, French Guiana by Ariane-5 VA-246. Weighing about 5854 kg, GSAT-11 is the heaviest satellite built by ISRO.
India’s second mission to Moon, Chandrayaan-2 was successfully launched on July 22, 2019 on board GSLV Mk III-M1, first operational flight of this new launch vehicle. Chandrayaan-2 Orbiter is providing valuable science data for the research community.
The launch of PSLV-C48/ RISAT-2BR1 in Dec 2019 marked the 50th launch of PSLV, the workhorse launch vehicle.
Quantum entanglement-based real-time Quantum Key Distribution (QKD) over 300m atmospheric channel along with quantum-secure text, image transmission and quantum-assisted two-way video calling was demonstrated on 27 January 2022.
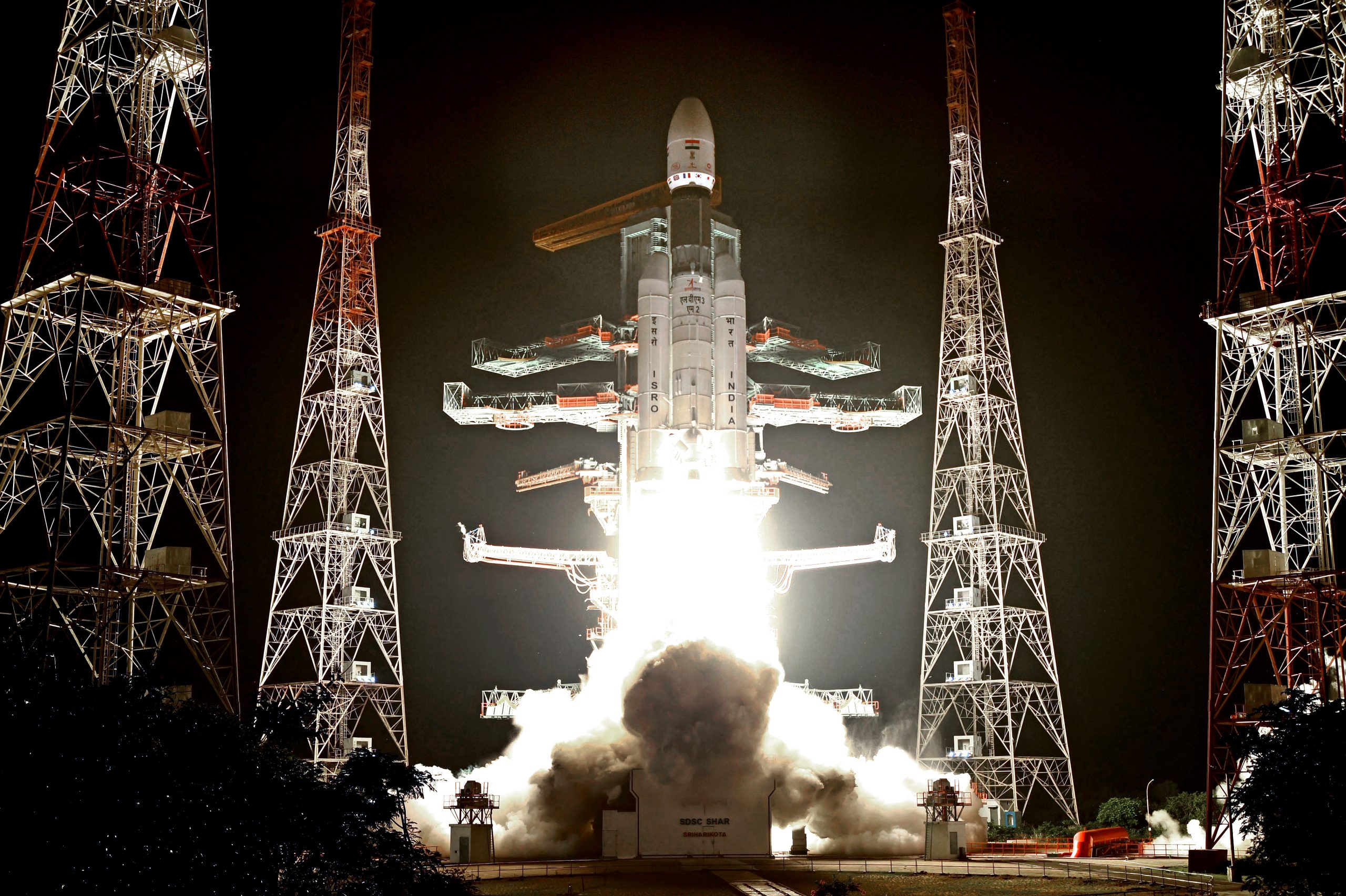
The Hon’ble Minister of State (Department of Space) dedicated ISRO System for Safe & Sustained Operations Management (IS4OM) to the nation in Jul-2022. LVM3 (GSLV MkIII) M2/OneWeb India-1 Mission was successfully accomplished on 23rd October 2022. With this launch, LVM3 exemplifies Atmanirbharata and enhances India’s competitive edge in the global commercial launch service market.
As part of the Gaganyaan programme, new Test Vehicle for testing critical systems is developed. ‘Integrated Main Parachute Airdrop Test (IMAT)’ of the crew module deceleration system was successfully carried out at Babina Field Fire Range (BFFR), Jhansi, Uttar Pradesh on 18th November 2022.
ISRO successfully demonstrated new technology with Inflatable Aerodynamic Decelerator (IAD) – a game changer with multiple applications for future missions.
Recently, PSLV-C54 was successfully launched EOS-06 satellite on 26th November 2022 along with Eight Nano-satellites including INDIA-BHUTAN SAT (INS-2B).